Wearing shoe inserts (orthotics) will help to prevent movements that are excessive in both amounts of movement and also in the speed of movement. For example, pronation at the incorrect time of the gait (walking) cycle or pronation that happens too rapidly will cause overuse of the foot, injury and foot pain.
Both types of pronation can be controlled with foot orthotics by adding additional arch support.
Functional foot orthotics alter the way the foot interacts with the ground. The aim of using a foot orthotic is to relieve the amount of strain on the foot which will reduce foot pain. This is achieved by supporting the anatomical arches of the foot.
Foot orthotics are most effective when worn with well-fitted supportive footwear. Even the most effective orthotic when placed into old worn-out shoes will not function to its maximum.
FOOT ORTHOTICS
“Ortho” is a Greek word meaning “to straighten”. Foot orthotics or foot orthoses are the devices used to support or/and straighten a foot to its natural position and improve foot function so that it functions correctly during the gait cycle.
To understand better the concept of foot orthotics, and how it helps to treat different foot and lower limb problems, the first one needs to know certain definitions.
Orthotics:
It is a branch of medical science that relates to the formation and application of orthosis or orthotic devices that are used to support and rectify the function of a part of the body whether the trunk or any limb. Foot orthotics relate to the problems of the foot and lower limb.
Orthotists:
Professionals trained in the field of orthotics and have a profound knowledge of anatomy, physiology, gait analysis, material engineering etc. An orthotist is a technician that designs and manufactures orthotics. An orthotist will help to custom fit an orthotic prescription to match your feet.
Podiatrist:
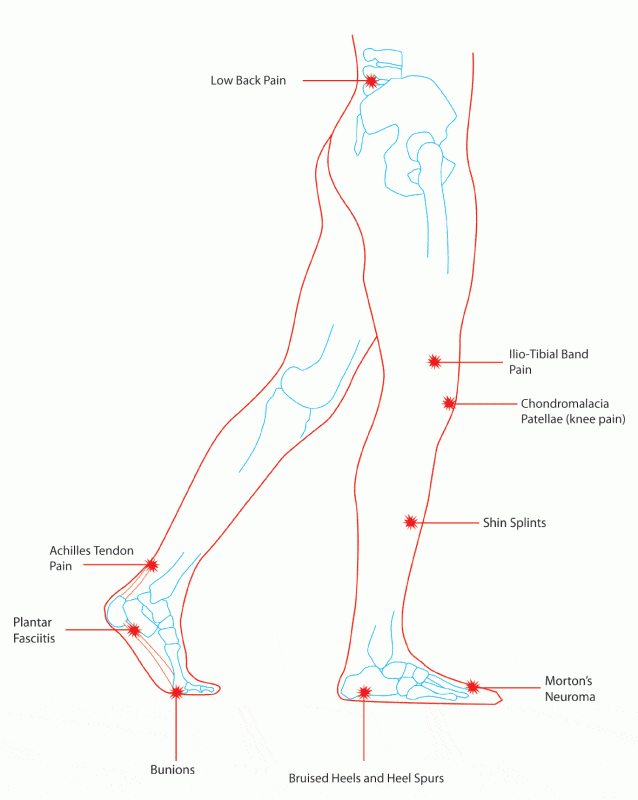
A podiatrist is a “foot specialist”, who deals with foot health and problems related to feet such as corns, bunions, heel spurs, arch problems, ingrown toenails, foot injuries, infections, and flat feet, deformities etc.
His job is to treat such problems with medication, physiotherapy, orthotics or surgery. When a patient is experiencing foot pain a podiatrist will assess the foot function of the patient and arrange an orthotic prescription to exactly match the patient’s issue and treat their foot pain.
Foot Biomechanics:
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the motion of bodies, in the case of Biomechanics, the bodies are living as bio = life. So, foot biomechanics basically, relates to the study of foot movements and the effects of muscles and gravity on its skeletal structure.
A foot can move upwards (dorsiflexion) and downwards (plantarflexion); horizontally outwards (Abduction) and horizontally inwards (Adduction); twist outwards (Eversion) and twist inwards (Inversion).